---
title: SFG4
subtitle: Survival Forest Graphs Within Treatment Arms by Continuous Biomarker Cutoff
categories: [SFG]
---
------------------------------------------------------------------------
::: panel-tabset
## Setup
We prepare the data similarly as in [SFG1](../graphs/SFG1/sfg01.qmd).
```{r, message = FALSE}
library(tern)
library(dplyr)
adtte <- random.cdisc.data::cadtte %>%
df_explicit_na() %>%
filter(
PARAMCD == "OS",
BEP01FL == "Y"
) %>%
mutate(
AVAL = day2month(AVAL),
AVALU = "Months",
is_event = CNSR == 0,
ARM_BIN = fct_collapse_only(
ARM,
CTRL = "B: Placebo",
TRT = c("A: Drug X", "C: Combination")
)
) %>%
var_relabel(
BEP01FL = "BEP",
BMRKR1 = "Biomarker (Countinuous)"
)
```
## Plot
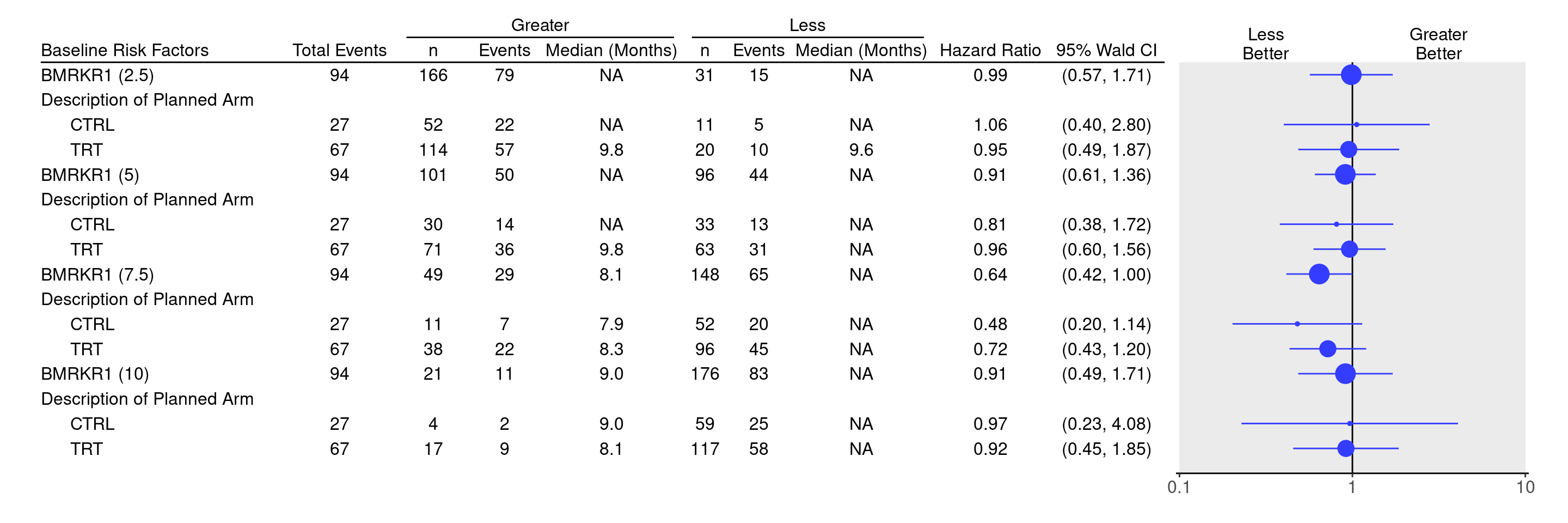
We define a vector of all cutpoints to use for a numeric biomarker (here `BMRKR1`).
We `lapply()` over this vector, each time generating a binary factor variable `BMRKR1_cut` and then tabulating the resulting statistics similar to [SFG3](../graphs/SFG3/sfg03.qmd), this time including the treatment arms in the `subgroups` argument.
Then we `rbind()` all tables in the list together.
```{r}
all_cutpoints <- c(2.5, 5, 7.5, 10)
tables_all_cutpoints <- lapply(all_cutpoints, function(cutpoint) {
adtte_cut <- adtte %>%
mutate(
BMRKR1_cut = explicit_na(factor(
ifelse(BMRKR1 > cutpoint, "Greater", "Less")
))
)
tbl <- extract_survival_subgroups(
variables = list(
tte = "AVAL",
is_event = "is_event",
arm = "BMRKR1_cut",
subgroups = "ARM_BIN"
),
label_all = paste0("BMRKR1 (", cutpoint, ")"),
data = adtte_cut
)
basic_table() %>%
tabulate_survival_subgroups(
df = tbl,
vars = c("n_tot_events", "n", "n_events", "median", "hr", "ci"),
time_unit = adtte_cut$AVALU[1]
)
})
result <- do.call(rbind, tables_all_cutpoints)
```
We can now produce the forest plot using the `g_forest()` function.
Similarly as in [SFG3](../graphs/SFG3/sfg03.qmd) we need to specify the `col_x`, `col_y` and `forest_header` arguments for `g_forest()` by recovering them from one of the original tables.
```{r, fig.width = 15}
one_table <- tables_all_cutpoints[[1]]
g_forest(
result,
col_x = attr(one_table, "col_x"),
col_ci = attr(one_table, "col_ci"),
forest_header = attr(one_table, "forest_header"),
col_symbol_size = attr(one_table, "col_symbol_size")
)
```
{{< include ../misc/session_info.qmd >}}
:::