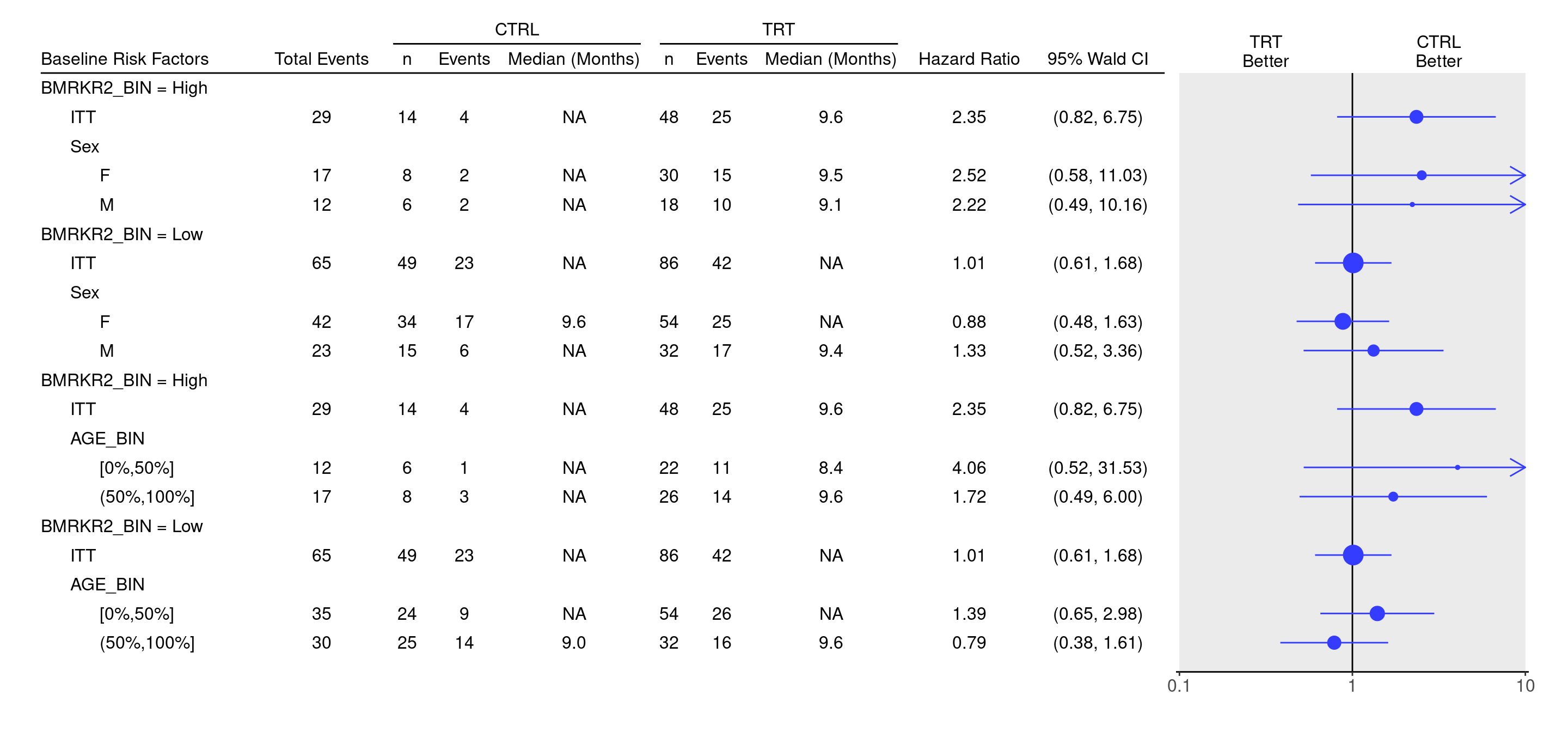
--- title: SFG5A subtitle: Survival Forest Graph Comparing Categorical Biomarker Groups on Subgroups categories: [SFG] --- ## Plot `col_info` is aligned across all subtables before using `rbind()` to combine subtables.`rbind()` does not work out of the box to combine subtables.)```{r} <- function (filter_var, filter_condition, sub_var) {<- adtte %>% filter (!! as.name (filter_var) == filter_condition)if (nrow (dataset) == 0 ) {stop (paste ("Subset" , filter_var, "==" , filter_condition, "is empty" ))<- extract_survival_subgroups (variables = list (tte = "AVAL" ,is_event = "is_event" ,arm = "ARM_BIN" ,subgroups = sub_varlabel_all = "ITT" ,data = datasetbasic_table () %>% tabulate_survival_subgroups (df = tbl,vars = c ("n_tot_events" , "n" , "n_events" , "median" , "hr" , "ci" ),time_unit = dataset$ AVALU[1 ]<- function (sub_tab, sub_title) {label_at_path (sub_tab, path = row_paths (sub_tab)[[1 ]][1 ]) <- sub_title<- list (tables_all (filter_var = "BMRKR2_BIN" , filter_condition = "High" , sub_var = "SEX" ),tables_all (filter_var = "BMRKR2_BIN" , filter_condition = "Low" , sub_var = "SEX" ),tables_all (filter_var = "BMRKR2_BIN" , filter_condition = "High" , sub_var = "AGE_BIN" ),tables_all (filter_var = "BMRKR2_BIN" , filter_condition = "Low" , sub_var = "AGE_BIN" )col_info (tables_list[[2 ]]) <- col_info (tables_list[[1 ]])<- rbind (add_subtitle (tables_list[[1 ]], "BMRKR2_BIN = High" ),add_subtitle (tables_list[[2 ]], "BMRKR2_BIN = Low" ),add_subtitle (tables_list[[3 ]], "BMRKR2_BIN = High" ),add_subtitle (tables_list[[4 ]], "BMRKR2_BIN = Low" )``` `g_forest()` function.```{r, fig.width = 15, fig.height = 7} one_table <- tables_list[[1]] g_forest( result, col_x = attr(one_table, "col_x"), col_ci = attr(one_table, "col_ci"), forest_header = attr(one_table, "forest_header"), col_symbol_size = attr(one_table, "col_symbol_size") ) ```